常用数据结构 前缀树 在计算机科学中,trie,又称前缀树或字典树 ,是一种有序树 ,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 type Trie struct { children map [rune ]*Trie isEnd bool } func NewTrie () return &Trie{children: make (map [rune ]*Trie)} } func (t *Trie) string ) { current := t for _, r := range word { if current.children[r] == nil { current.children[r] = &Trie{children: make (map [rune ]*Trie)} } current = current.children[r] } current.isEnd = true } func (t *Trie) string ) bool { current := t for _, r := range word { if current.children[r] == nil { return false } current = current.children[r] } return current.isEnd }
LeetCode范例:
注意事项:isEnd 位于当前节点的下一节点,即 a->b->c->isEnd
并查集 常见题型 数组 数组子集问题 剑指 Offer II 079. 所有子集 - 力扣(Leetcode) n = nums.length,由于 n <= 10,数组长度不长,所以可以考虑用一串长度为 n 的二进制串来表示各位要不要取(0:不取,1:取),那么共有 $2^n$ 种状态,以 nums = [1, 2, 3] 为例:
二进制串
子数组
二进制串对应十进制数
000
[]
0
001
[3]
1
010
[2]
2
011
[2,3]
3
100
[1]
4
101
[1,3]
5
110
[1,2]
6
111
[1,2,3]
7
那么遍历每种状态即可
代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 func subsets (nums []int ) int { ans := [][]int {} n := len (nums) for i := 0 ; i < (1 << n); i++ { subArr := []int {} for j := 0 ; j < n; j++ { if i & (1 << j) > 0 { subArr = append (subArr, nums[j]) } } ans = append (ans, subArr) } return ans }
数组全排列 46. 全排列 - 力扣(LeetCode) 回溯算法 ,在解决之前最好先自己画一下回溯树 来捋清楚关系!
图片来自46. 全排列 题解 - 力扣(LeetCode)
回溯模板:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 func backtrack () if 满足终止条件 { 将当前结果添加到最终结果中 return } for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) { 处理节点 backtrack() 回溯,撤销处理结果 } }
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 func permute (nums []int ) int { res := [][]int {} n := len (nums) path := make ([]int , 0 ) visited := make ([]bool , n) var backtrack func () backtrack = func () if len (path) == n { tmp := make ([]int , n) copy (tmp, path) res = append (res, tmp) return } for i, num := range nums { if visited[i] { continue } path = append (path, num) visited[i] = true backtrack() path = path[:len (path)-1 ] visited[i] = false } } backtrack() return res }
数组中第 K 个最大元素 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode) 7-2「力扣」第 215 题:数组中的第 K个最大元素_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 快速排序 ,时间复杂度也只能是 $O(nlogn)$,无法达到题目要求的 $O(n)$,故可以在快排的基础上进行改进(快速选择),来达到 $O(n)$ 的复杂度。
我们知道快排中的 patition 是用来选出一个枢轴元素(pivot),将数组中的元素划分为大于 nums[pivot] 及小于 nums[pivot]两部分,如果此时的 pivot 正好等于 $n-k$ ,则说明此时的 pivot 处的元素就是第 $k$ 大元素。循着这个逻辑就可以利用二分思想缩小范围,直到 pivot 正好等于 $n-k$。
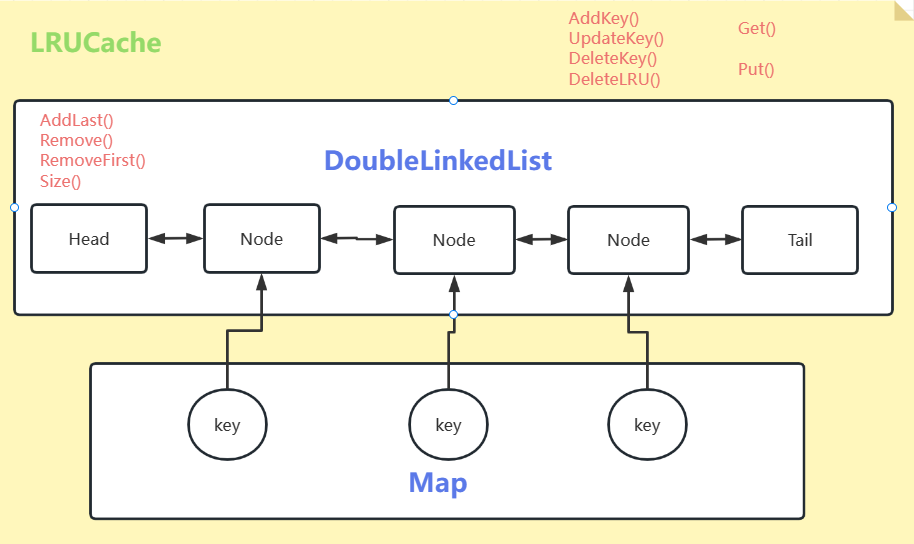
链表 LRU 缓存 146. LRU 缓存 - 力扣(LeetCode)
实现 LRUCache 主要需要用到哈希链表 ,所以本题也可以转换为实现一个 LinkedHashMapMap 和一个 双向链表 组成,双向链表是有序的,Map 可以帮助快速访问到链表中的结点。双向链表中包含了 Cache 中所需的 key、val 字段,Map 对 key 及对应的结点进行了映射 (key -> *Node)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 type Node struct { key int value int next *Node pre *Node } type DoubleLinkedList struct { head *Node tail *Node size int } func InitList () head, tail := &Node{key:0 ,value:0 }, &Node{key:0 ,value:0 } head.next = tail tail.pre = head return DoubleLinkedList{ head: head, tail: tail, size: 0 , } } func (dll *DoubleLinkedList) pre := dll.tail.pre pre.next = node node.pre = pre node.next = dll.tail dll.tail.pre = node dll.size++ } func (dll *DoubleLinkedList) node.pre.next = node.next node.next.pre = node.pre dll.size-- } func (dll *DoubleLinkedList) if dll.head.next == dll.tail { return nil } first := dll.head.next dll.Remove(first) return first } func (dll *DoubleLinkedList) int { return dll.size } type LRUCache struct { mp map [int ]*Node cache DoubleLinkedList capacity int } func Constructor (capacity int ) return LRUCache{ mp: make (map [int ]*Node), cache: InitList(), capacity: capacity, } } func (this *LRUCache) int ) { node := this.mp[key] this.cache.Remove(node) this.cache.AddLast(node) } func (this *LRUCache) int ) { node := &Node{ key: key, value: val, } this.cache.AddLast(node) this.mp[key] = node } func (this *LRUCache) int ) { node := this.mp[key] this.cache.Remove(node) delete (this.mp, key) } func (this *LRUCache) LRUNode := this.cache.RemoveFirst() delete (this.mp, LRUNode.key) } func (this *LRUCache) int ) int { if this.mp[key] == nil { return -1 } this.UpdateKey(key) return this.mp[key].value } func (this *LRUCache) int , value int ) { if this.mp[key] != nil { this.DeleteKey(key) this.AddKey(key, value) return } if this.cache.Size() >= this.capacity { this.DeleteLRU() } this.AddKey(key, value) }
动态规划 最长递增子序列 300. 最长递增子序列 - 力扣(LeetCode) 动态规划 方法或者贪心 算法,本题使用动态规划算法
定义状态
转台转移方程
初始化
输出
空间优化1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 func lengthOfLIS (nums []int ) int { n := len (nums) if n == 1 { return n } res := 0 dp := make ([]int , n) for i := range dp { dp[i] = 1 } for i := 1 ; i < n; i++ { for j := 0 ; j < i; j++ { if nums[j] < nums[i] { dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ) } } } for _, num := range dp { res = max(res, num) } return res }
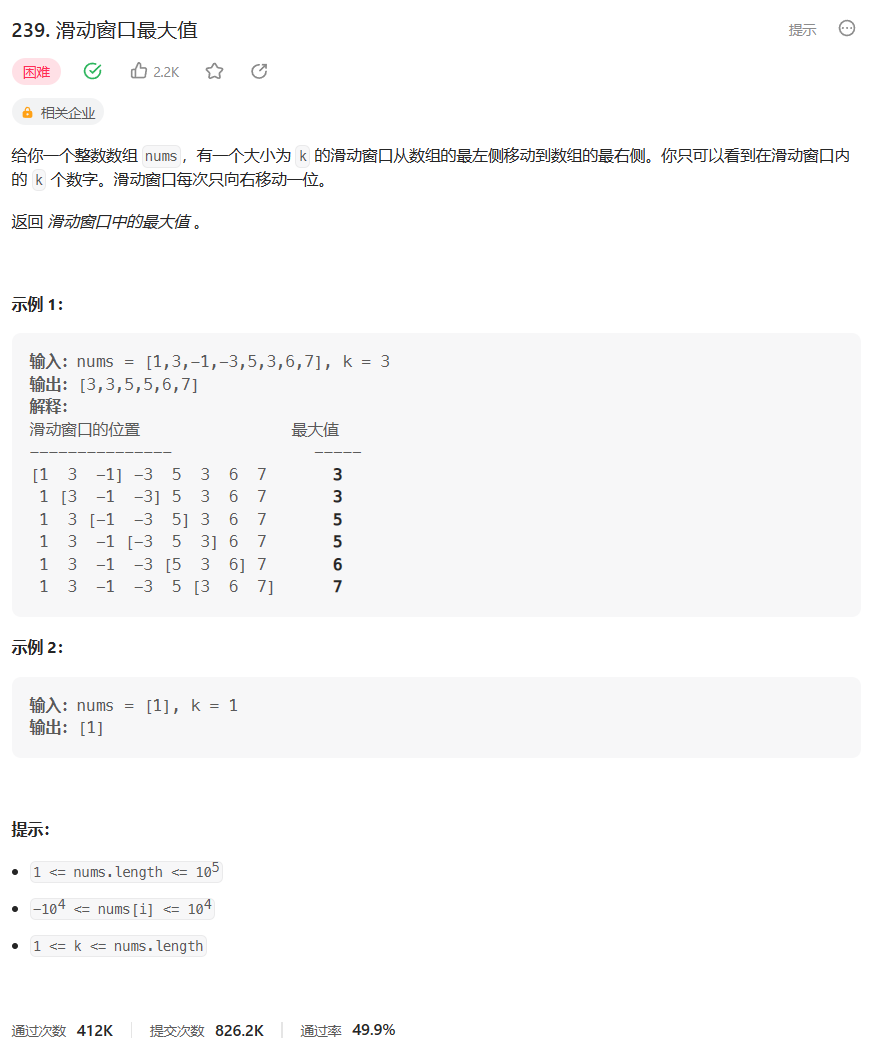
滑动窗口 滑动窗口的最大值 239. 滑动窗口最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
使用优先队列 (堆)存储滑动窗口中最大值的下标,然后滑动窗口每次移动,调整堆中的元素
使用单调栈 !维护一个单调递减的栈。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 type dq struct { queue []int } func InitDQ () return &dq{ queue: make ([]int , 0 ), } } func (q *dq) int { return q.queue[0 ] } func (q *dq) int { return q.queue[len (q.queue)-1 ] } func (q *dq) bool { return len (q.queue) == 0 } func (q *dq) int ) { for !q.Empty() && val > q.Rear() { q.queue = q.queue[:len (q.queue)-1 ] } q.queue = append (q.queue, val) } func (q *dq) int ) { if !q.Empty() && val == q.Front() { q.queue = q.queue[1 :] } return } func maxSlidingWindow (nums []int , k int ) int { queue := InitDQ() n := len (nums) res := make ([]int , 0 ) for i := 0 ; i < k; i++ { queue.Push(nums[i]) } res = append (res, queue.Front()) for i := k; i < n; i++ { queue.Pop(nums[i-k]) queue.Push(nums[i]) res = append (res, queue.Front()) } return res }